Automation storage equipment series
- Category : Automation storage equipment series
- Custom service : Yes
- Payment : L/C, T/T, Western Union, D/P, MoneyGram
- Place of delivery : NanJing, China
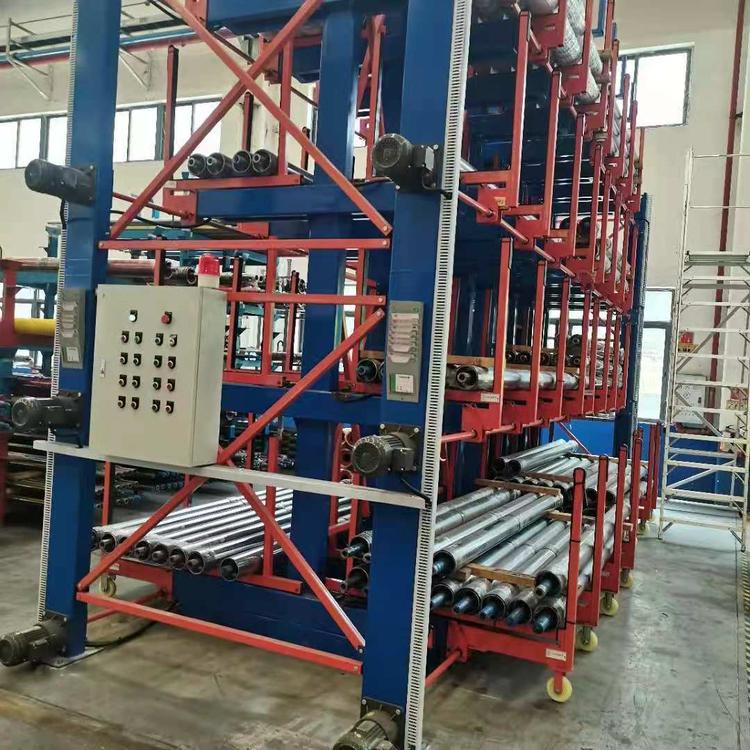
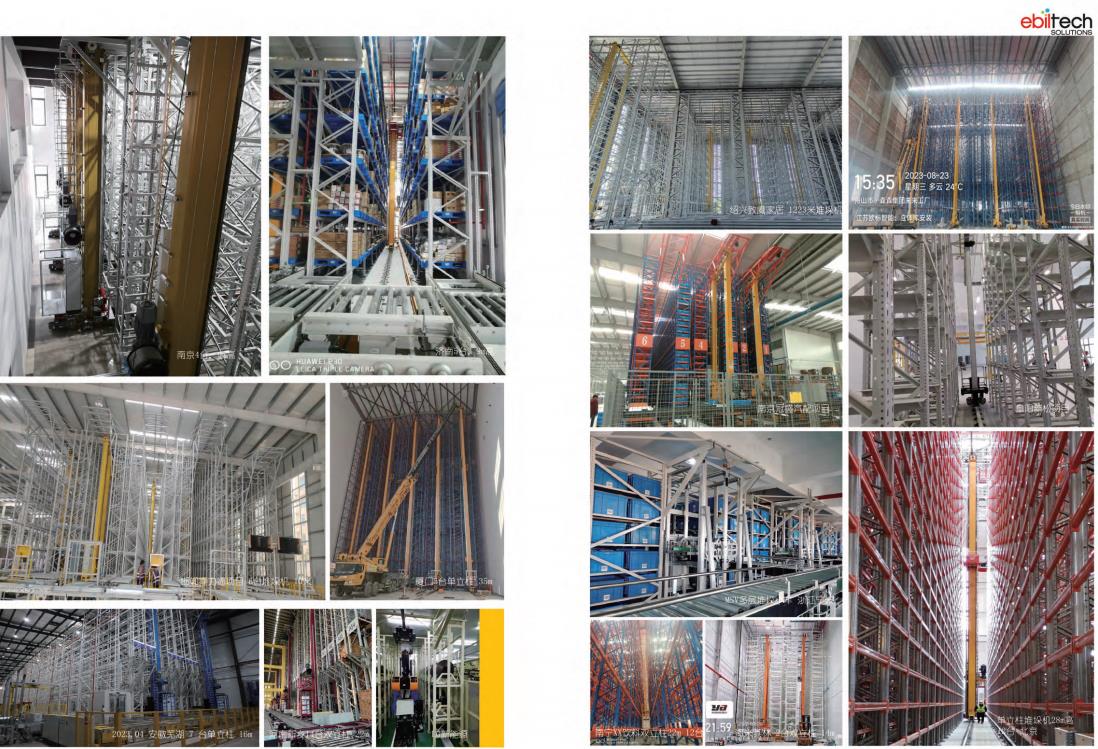
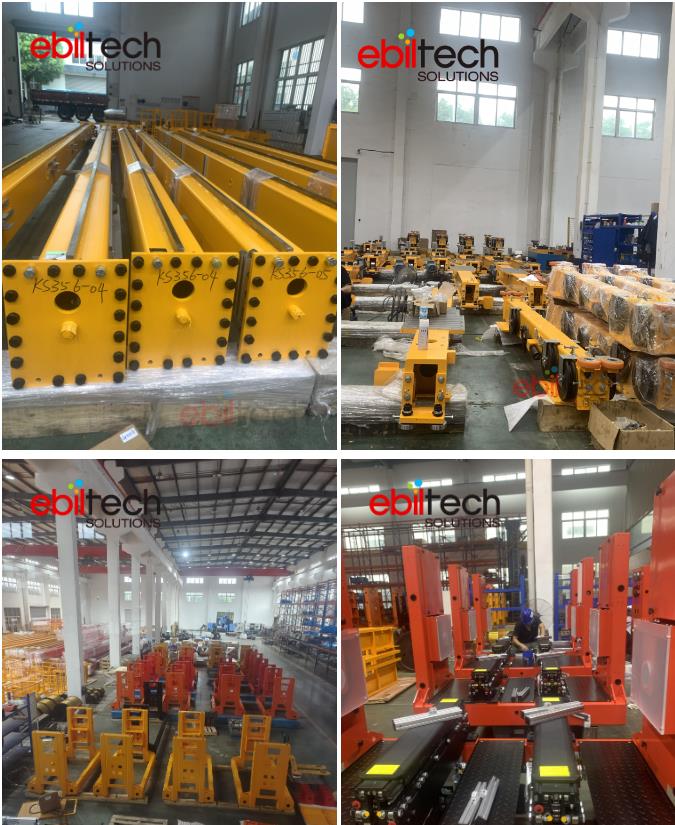
Stacker Crane
Ebil Tech
provide professional automated warehouse solutions
The EBILTECH stacker cranes automate product input and output operations, ensuring fast and precise control of warehouse stock and eliminating manual operating errors.
The key benefits of using stacker cranes within a storage system are:
1. Automation of the product input and output operations
2 .Fast and accurate warehouse controls and updates, facilitating the inventory system
3. Elimination of manual errors
4. he possibility of adjusting to special working conditions (temperature -30°, high humidity)
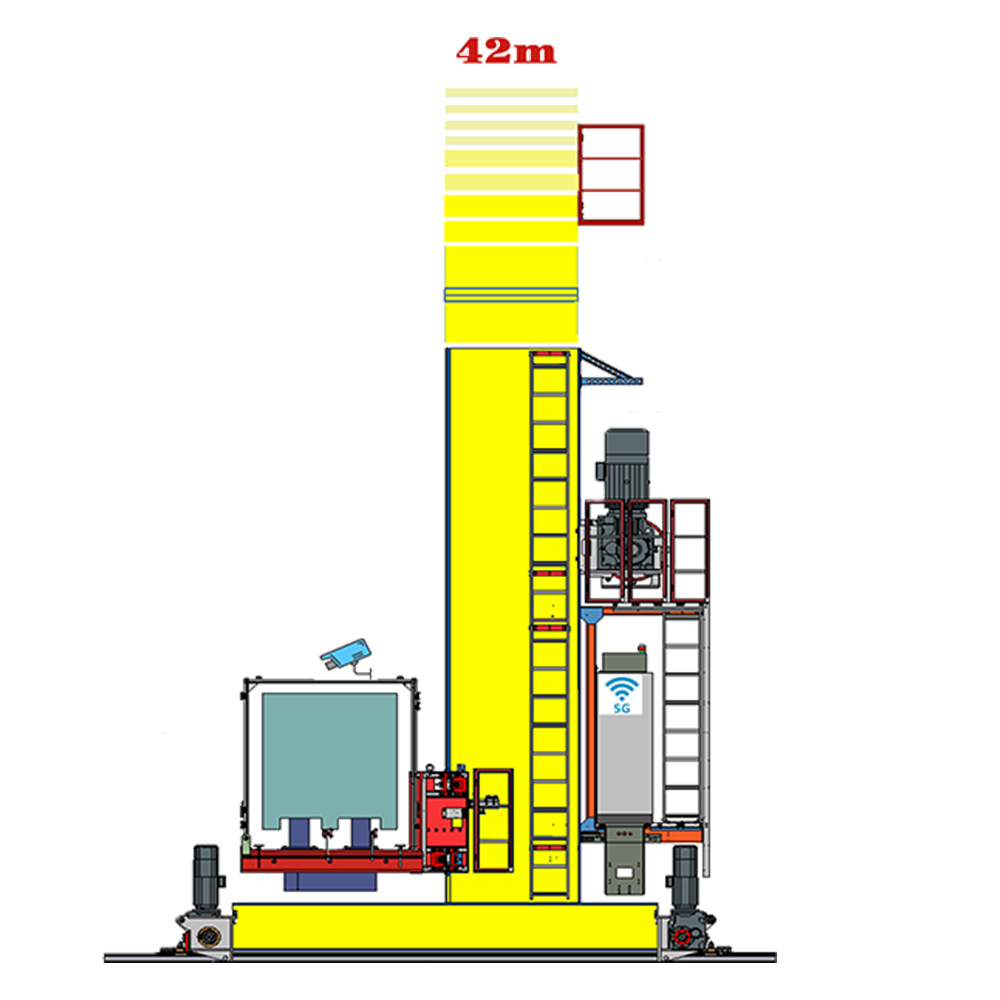
Stacker Cranes For Warehouse
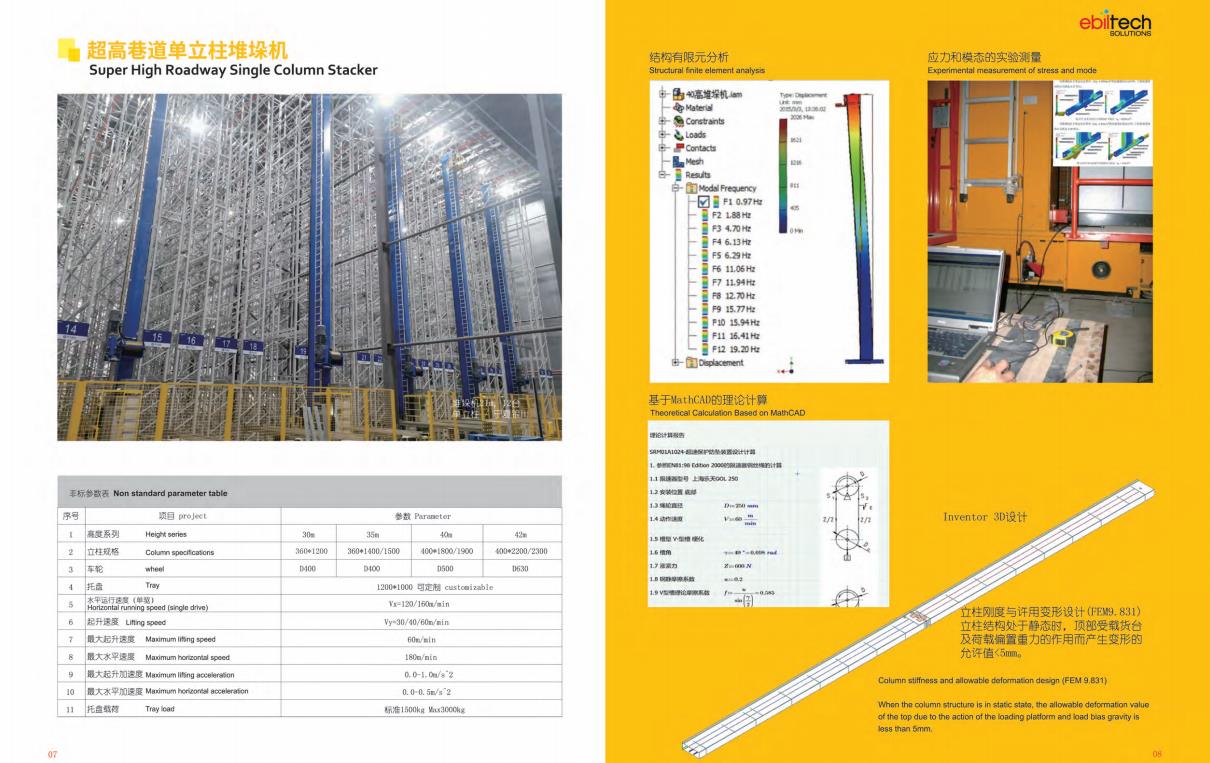
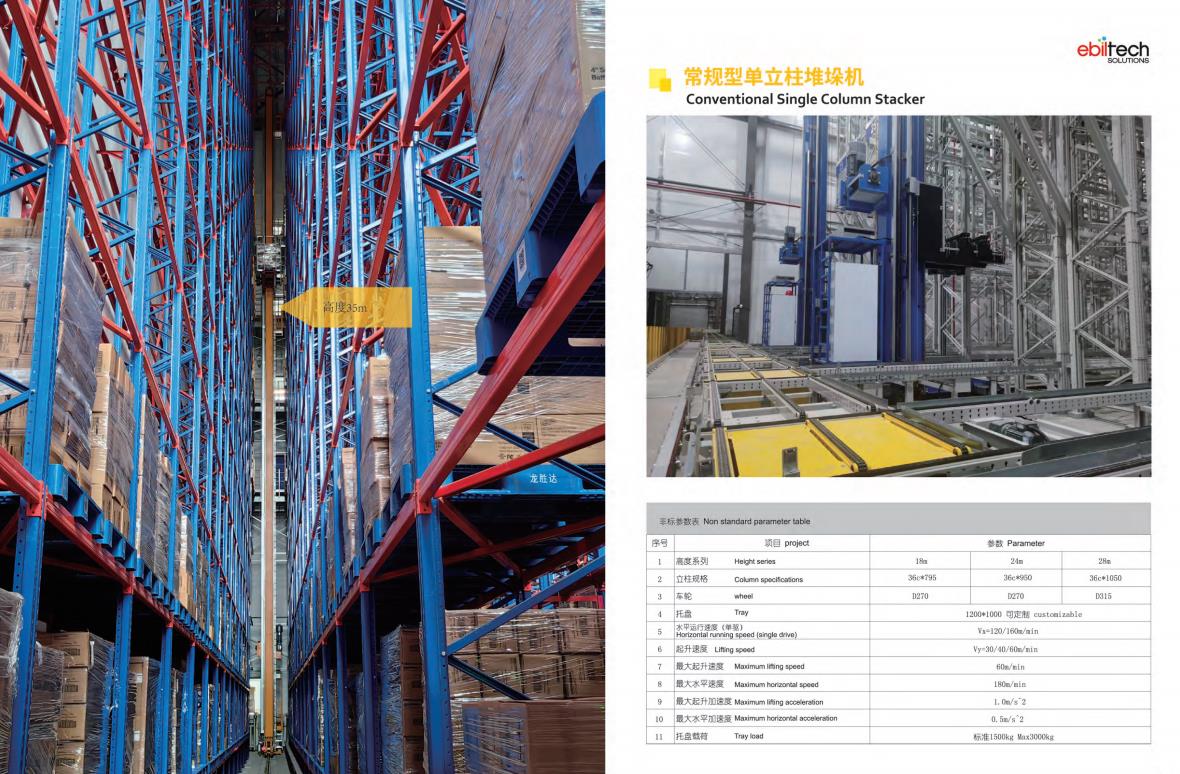
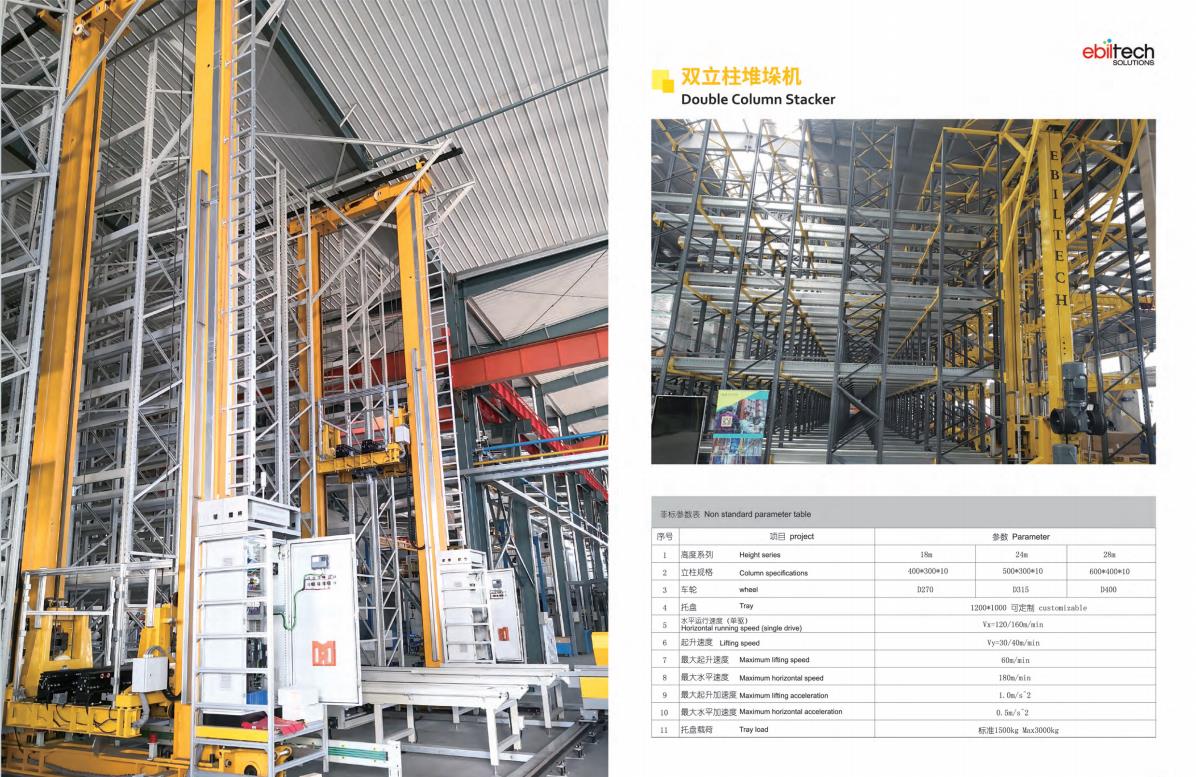
type:Single Column Stacker,Double Column Stacker,Heavy Stacker,Miniload Stacker Crane
Loading: 500-1000kg,500-1500kg,Loading: 2000-3500kgLoading: 20-50kg
Height: <=12mHeight: <=24mHeight:<=16 mmHeight: <=18 m
Speed: 180m/min,Speed: 180m/min,Speed: 80m/min,Speed: 240m/min






Get a quote
The professional supplier that provide intelligent intensive storage equipment and system solutions.