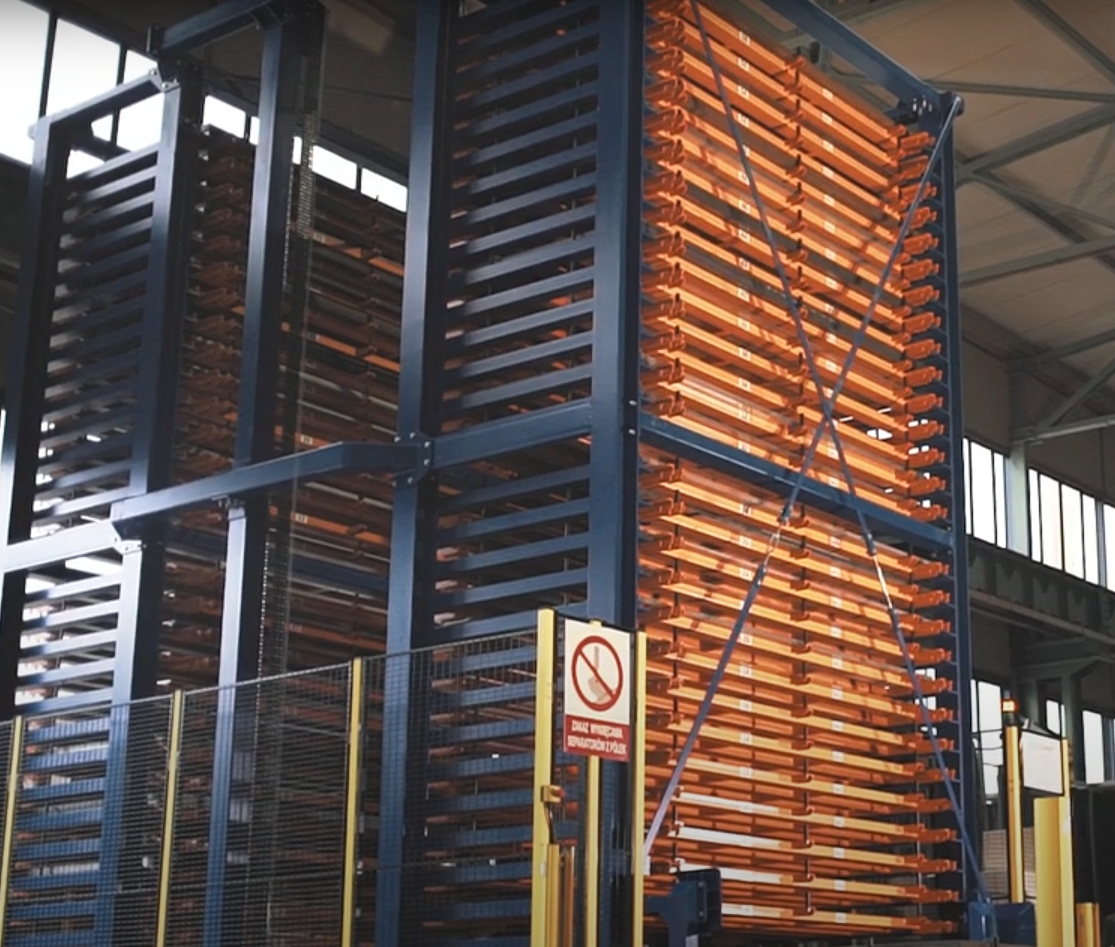
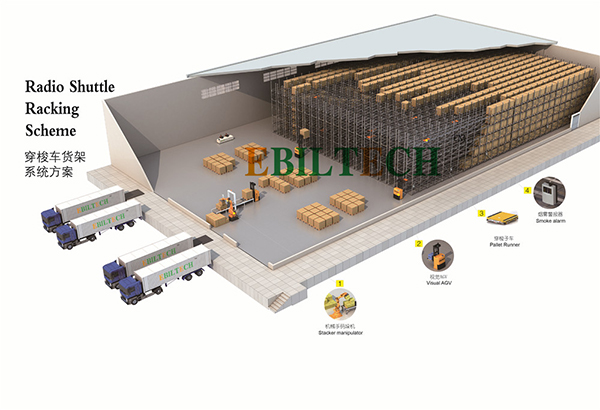
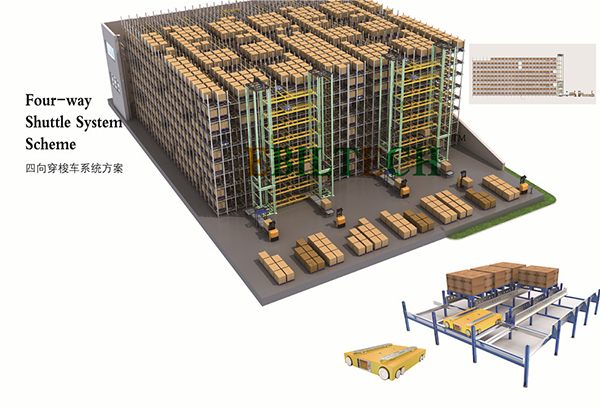
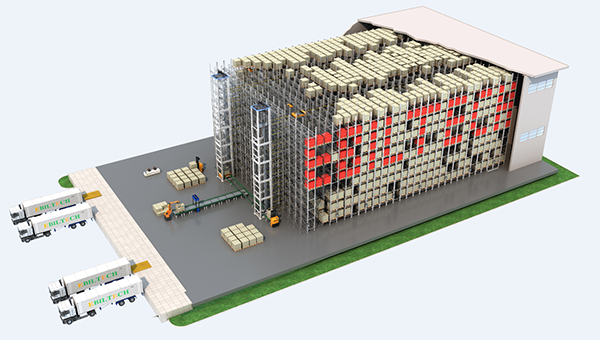
Products
Ebil Tech
Automated Warehouse
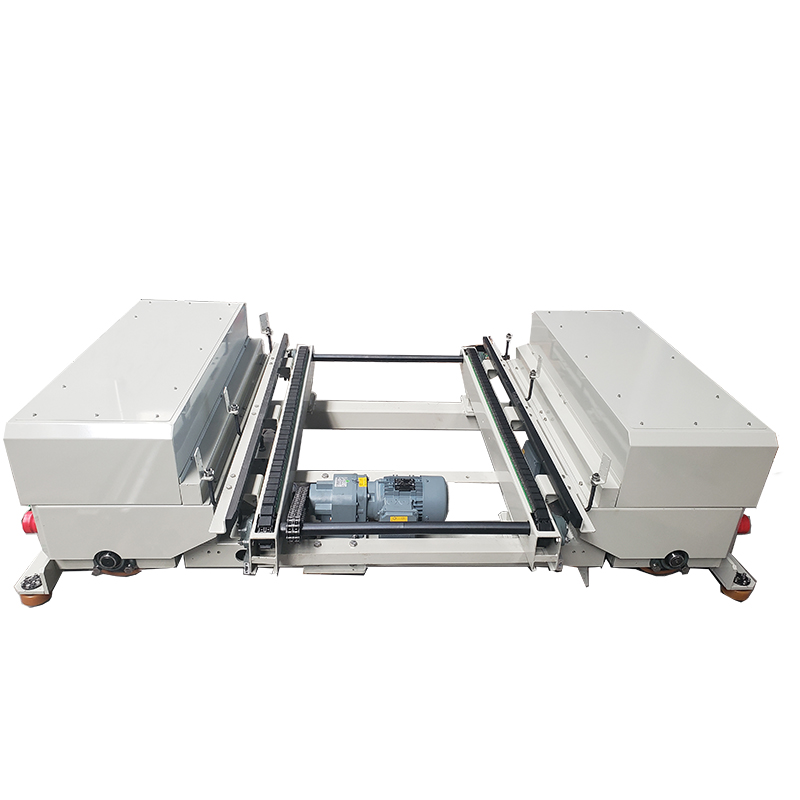
Automated Warehouse is one of our products, we can provide one-stop storage system solutions and products, our products also include Multi-Lever Mezzanine Racking, Warehouse Racking, Warehouse Shuttle Car, VNA Selective Rack, Narrow Aisle Warehouse Rack, Shuttle System With Satellite Shuttles, Very Narrow Aisle Pallet Racking, Mezzanine Floors, and so on. EBILTECH providing the automated and intelligent products of logistics system, such as pallet shuttle, stacker crane, cargo elevator, automatic transport system, other electrical automation and software of the logistics system. We have many main markets in the world, such as Puerto Rico, Albania, Djibouti, Minsk (Belarus), New Zealand, Syria, and so on. We are looking forward to cooperate with you. If you are interested in Automated Warehouse.
About Automated Warehouse
Automated warehouse is a new concept emerging in logistics warehousing. The use of three-dimensional warehouse equipment can realize the rationalization of high-level warehouses, automated access, and simplified operations; automated warehouses are currently the most technically advanced form. The main body of the automated warehouse consists of shelves, tunnel stacking cranes, entry (exit) workbench and automatic entry (exit) and operation control systems. The shelf is a building or structure with a steel structure or reinforced concrete structure. Inside the shelf is a standard-sized cargo space. The lane stacking crane travels through the lanes between the shelves to complete the work of storing and picking up goods. Computer and barcode technology are used in management.
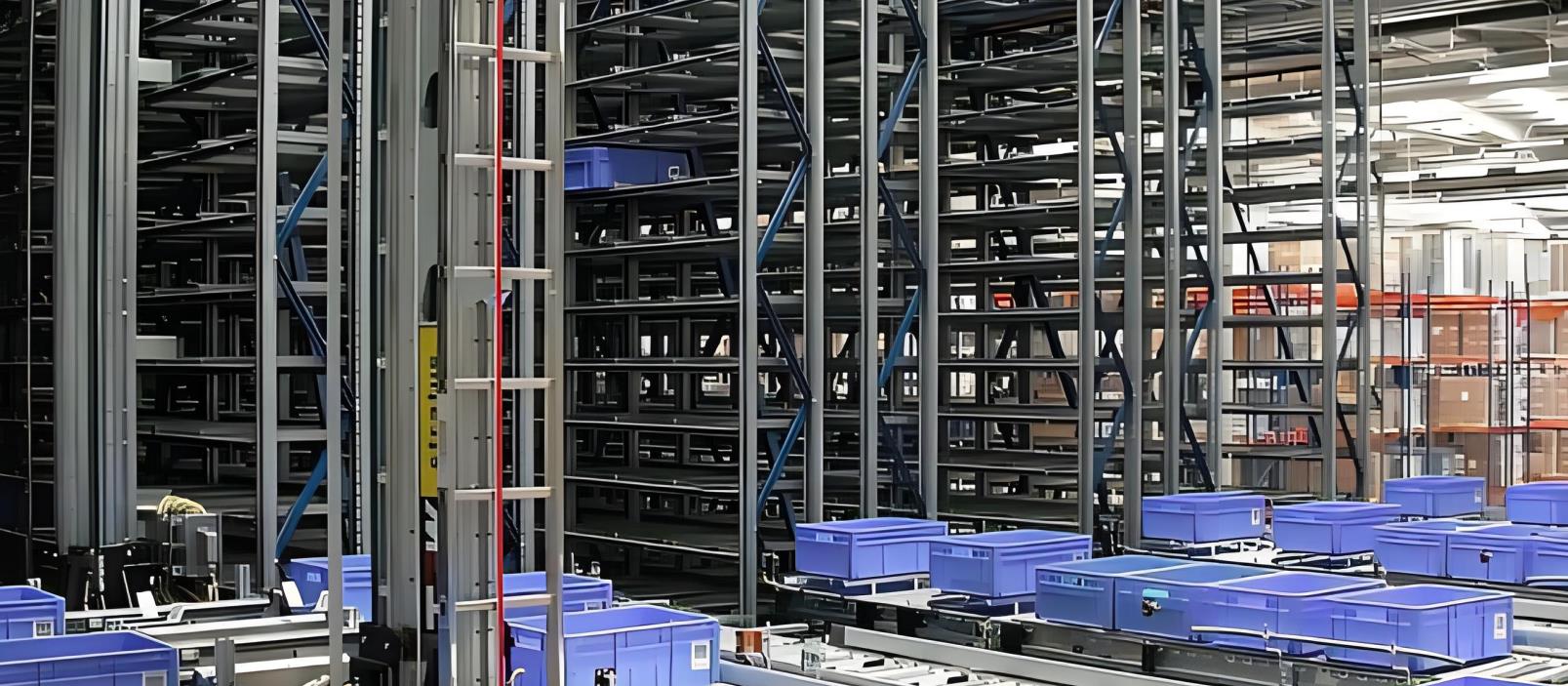

Basic introduction
The emergence and development of warehouses are the result of the development of production and technology after World War II. In the early 1950s, three-dimensional warehouses using bridge-type stacking cranes appeared in the United States; in the late 1950s and early 1960s, three-dimensional warehouses with driver-operated lane-type stacking cranes appeared; in 1963, the United States took the lead in using computer control technology in elevated warehouses and established The first computer-controlled three-dimensional warehouse was built. Since then, automated warehouses have developed rapidly in the United States and Europe, and formed a specialized discipline. In the mid-1960s, Japan began to build three-dimensional warehouses, and the development speed is getting faster and faster, becoming one of the countries with the most automated warehouses in the world today.
China's development of three-dimensional warehouses and material handling equipment was not late. In 1963, it developed the first bridge-type stacking crane. In 1973, it began to develop China's first computer-controlled automated warehouse (15 meters high). The library was put into operation in 1980. As of 2003, the number of automated warehouses in China has exceeded 200. Three-dimensional warehouses have become an indispensable warehousing technology for enterprise logistics and production management due to their high space utilization, strong entry and exit capabilities, and the use of computers for control and management, which are beneficial to enterprises in implementing modern management. Enterprise's attention.
Automated warehouse ( AS/RS ) is composed of three-dimensional shelves, rail lane stackers, inbound and outbound pallet conveyor systems, size detection barcode reading systems, communication systems, automatic control systems, computer monitoring systems, computer management systems and others such as A complex automation system composed of auxiliary equipment such as wire and cable bridge distribution cabinets, pallets, adjustment platforms, steel structure platforms, etc. Apply the first-class integrated logistics concept, adopt advanced control, bus, communication and information technology, and carry out warehousing and warehousing operations through the coordinated actions of the above equipment.
Classification
building
According to the architectural form, it can be divided into two types: integral type and separate type.
(1) Integral type: In addition to storing goods, the shelves also serve as the supporting structure of the building and form part of the building, that is, the integrated structure of the warehouse shelves. Generally, the overall height is more than 12 meters. This kind of warehouse structure is light in weight, has good integrity and has good earthquake resistance.
(2) Detached type: In the detached type, the shelves for storing goods exist independently inside the building. The detached height is below 12 meters, but there are also 15 to 20 meters. It is suitable for using existing buildings as warehouses, or building a single high shelf in factories and warehouses.
Goods storage
According to the form of goods access, it is divided into unit rack type, mobile rack type and picking rack type.
(1) Unit shelf type: Unit shelf type is a common warehouse form. The goods are first placed on pallets or containers, and then loaded into the cargo spaces of the unit shelves.
(2) Mobile shelf type: The mobile shelf type consists of electric shelves. The shelves can walk on the track, and the control device controls the closing and separation of the shelves. During operation, the shelves can be separated and work can be carried out in the tunnel; when not in operation, the shelves can be closed, leaving only one working tunnel, thereby improving space utilization.
(3) Picking rack type: The sorting mechanism is the core part of the picking rack type, which is divided into two methods: in-lane sorting and outside-lane sorting. "Pick before arrival" means that the picker takes the picking stacker to the goods grid and picks the required number of goods from the goods grid to leave the warehouse. "Goods-to-person picking" means that pallets or boxes containing the required goods are transported from the stacker to the picking area. The picking personnel pick out the required goods according to the requirements of the bill of lading, and then return the remaining goods to the original place.
Shelf structure
It can be divided into unit format, through type, horizontal rotating type and vertical rotating type.
(1) Unit cargo format warehouse: similar to the unit shelf type, with lanes occupying about one-third of the area.
(2) Through-type: In order to improve the utilization rate of the warehouse, the lanes between each row of shelves can be eliminated, and the individual shelves can be merged together so that the goods on each floor and in the same column can communicate with each other, forming a warehouse that can store multiple units of goods at one time. Passage, and at the other end the goods are picked up by the outgoing crane, becoming a through-type warehouse. According to the movement mode of cargo units in the channel, through-type warehouses can be divided into gravity rack warehouses and shuttle trolley rack warehouses. Each inventory channel of the gravity rack warehouse can only store the same kind of goods, so it is suitable for warehouses where the variety of goods is not too many but the quantity is relatively large. Shuttle trolleys can be moved by cranes from one inventory aisle to another.
(3) Shelves of horizontal rotary warehouses: This type of warehouse itself can run back and forth along a circular route in the horizontal plane. Each group of shelves consists of several independent containers, which are connected in series with a chain conveyor. There are support rollers below each container and guide rollers on the top. When the conveyor is running, the containers move accordingly. When you need to pick up a certain kind of goods, you only need to give the outbound instructions on the operation console. When the container containing the required goods is transferred to the outlet, the shelf stops running. This kind of rack is very suitable for picking small items. It is simple and practical, makes full use of space, and is suitable for occasions where the operating frequency is not too high.
(4) Vertical rotating rack warehouse: It is similar to the horizontal rotating rack warehouse, except that the rotation in the horizontal plane is changed to the rotation in the vertical plane. This kind of rack is especially suitable for storing long rolls of goods, such as carpets, floor leather, film rolls, cable rolls, etc.
Cost of building an automated warehouse
The cost of building an automated warehouse can vary significantly depending on various factors, including the size of the facility, level of automation, technology used, and specific requirements of the operation. It's important to note that providing an exact price is challenging without specific details, as costs can vary greatly.
The cost of building an automated warehouse typically includes the following components
1. Facility Construction: The cost of constructing the physical building, including the structure, flooring, walls, roofing, lighting, HVAC systems, and other necessary infrastructure. Construction costs can vary depending on factors such as location, size, and complexity of the facility.
2. Racking and Storage Systems: The cost of installing racking systems, shelving, and storage units to accommodate the inventory. This cost can vary based on the type of racking system, storage capacity, and customization requirements.
3. Automation Equipment: The cost of automation equipment, such as automated conveyor systems, robotic systems, sorting equipment, picking systems, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), shuttle systems, and other machinery required for material handling and storage automation.
4. Control Systems and Software: The cost of implementing control systems, software, and integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) or Warehouse Control Systems (WCS). This includes the cost of hardware, software licenses, and customization or configuration based on the specific needs of the operation.
5. Electrical and Mechanical Installations: The cost of electrical systems, including wiring, lighting, power distribution, and electrical panel installations. Additionally, the cost of mechanical systems, such as plumbing, fire suppression, and ventilation, should be considered.
6. Safety and Security Systems: The cost of implementing safety and security measures, including surveillance cameras, access control systems, fire detection and suppression systems, and other necessary safety equipment.
7. Project Management and Consulting: The cost of project management services, consulting fees, and professional services required for designing, engineering, and overseeing the construction and implementation of the automated warehouse.
It's important to note that these costs can vary significantly depending on the complexity and scale of the project. Generally, building an automated warehouse can range from several million dollars to tens of millions of dollars or more, depending on the size and level of automation. Large-scale, highly automated warehouses with advanced technologies can involve substantial investments.
Examples of automated warehouses and their estimated costs
1. Example 1: Small-Scale Automated Warehouse
- Facility Size: 10,000 square feet
- Level of Automation: Basic conveyor system, limited robotic assistance
- Estimated Cost Range: $2 million to $5 million
2. Example 2: Medium-Scale Automated Warehouse
- Facility Size: 50,000 square feet
- Level of Automation: Conveyor systems, robotic picking, automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS)
- Estimated Cost Range: $10 million to $20 million
3. Example 3: Large-Scale Automated Warehouse
- Facility Size: 200,000 square feet
- Level of Automation: Extensive conveyor systems, advanced robotics, shuttle systems, AS/RS, high-level warehouse control system integration
- Estimated Cost Range: $30 million to $50 million
Please note that these are rough estimates and the actual costs can vary significantly based on factors such as location, construction materials, labor costs, equipment selection, customization requirements, and other project-specific considerations. It's important to consult with professionals in the field to obtain accurate cost estimates tailored to your specific needs and project scope.
Technical performance
design
The design of each automated warehouse is divided into several main stages, and each stage has its own goals to achieve.
(1) Preparatory work before design
1. It is necessary to understand the on-site conditions for building a warehouse, including meteorology, topography, geological conditions, ground bearing capacity, wind and snow loads, earthquake conditions and other environmental influences.
2. In the overall design of automated warehouses, multiple disciplines such as machinery, structure, electrical, and civil engineering overlap and restrict each other. This requires third-party logistics companies to consider the needs of each discipline when designing. For example, the movement accuracy of machinery should be selected based on the accuracy of structural fabrication and the settlement accuracy of civil engineering.
3. It is necessary to formulate third-party logistics companies ' investment and staffing plans for warehousing systems to determine the scale and degree of mechanization and automation of the warehousing system.
4. It is necessary to investigate and understand other conditions related to the warehousing system of the third-party logistics company, such as the source of the goods, the traffic conditions connecting the warehouse, the packaging of the goods, the method of transporting the goods, the final destination of the goods and the means of transportation, etc.
(2) Selection and planning of storage areas
The selection and layout of the warehouse are of great significance to the infrastructure investment, logistics costs, labor conditions, etc. of the warehousing system. Considering urban planning and the overall operation of third-party logistics companies, it is best to choose an automated warehouse close to transportation hubs such as ports, docks, and freight stations, or close to production areas or raw material origins, or close to major sales markets. This can greatly Reduce costs for third-party logistics companies. Whether the location of the warehouse is reasonable will also have a certain impact on environmental protection, urban planning, etc. For example, if you choose to build an automated warehouse in a commercial area subject to traffic restrictions, on the one hand it will not be in harmony with the bustling business environment, and on the other hand you will have to pay a high price to purchase land. The most important thing is that due to traffic restrictions, goods can only be delivered in the middle of the night every day, which is obviously extremely unreasonable.
(3) Determine the warehouse form, operating methods and mechanical equipment parameters
The form of the warehouse needs to be determined based on the investigation of the types of goods entering the warehouse. Generally, unit cargo format warehouses are used. If the types of goods stored are single or small, and the batches of goods are large, gravity racks or other forms of through-type warehouses can be used. Determine whether stacking and picking operations are required based on the process requirements for inbound and outbound warehouses (whole unit or scattered inbound and outbound warehouses). If picking operations are required, determine the method of picking operations.
There is another operating method that is often used in automated warehouses. This is the so-called "free cargo space" method, that is, goods can be put into the warehouse nearby. Especially for goods that are frequently in and out of the warehouse and are overlong and overweight, they should be stored as close as possible to the warehouse. Work near the location of goods and delivery. This can not only shorten the time of entering and exiting the warehouse, but also save transportation costs.
There are many types of mechanical equipment used in automated warehouses, generally including lane stackers, continuous conveyors, high-rise shelves, and automatic guided vehicles with a high degree of automation. When carrying out the overall design of the warehouse, the most suitable mechanical equipment should be selected based on the scale of the warehouse, the variety of goods, the frequency of entry and exit, etc., and the main parameters of these equipment should be determined.
(4) Determine the form and specifications of the cargo unit
Since the premise of automated warehouse is unitized handling, determining the form, size and weight of the cargo unit is a very important issue. It will affect the investment in warehouses by third-party logistics companies, and will also affect the equipment and facilities of the entire warehousing system. Therefore, in order to reasonably determine the form, size and weight of the cargo unit, all possible cargo unit forms and specifications should be listed based on the results of surveys and statistics, and a reasonable selection should be made. For those goods with special shapes and sizes or that are very heavy, they can be handled individually.
(5) Determine the library capacity (including cache area)
Warehouse capacity refers to the number of units of goods that the warehouse can accommodate at the same time, which is a very important parameter for automated warehouses. Since the inventory cycle is affected by many unexpected factors, the peak value of the inventory sometimes greatly exceeds the actual storage capacity of the automated warehouse. In addition, some automated warehouses only consider the capacity of the shelf area, but ignore the area of the buffer area. As a result, the area of the buffer area is insufficient, making it impossible for goods in the shelf area to come out and goods outside the warehouse to enter.
(6) Distribution of warehouse area and other areas
Since the total area is fixed, many third-party logistics companies only pay attention to the office and experimental (including R&D) areas when building automated warehouses, but ignore the warehouse area. This has resulted in this situation, that is, in order to meet the warehouse capacity requirements If necessary, we can only meet the requirements by developing into space. But the higher the shelves, the higher the purchase and operating costs of machinery and equipment. In addition, since the optimal logistics route in an automated warehouse is linear, the warehouse design is often limited by the plane area, resulting in a circuitous logistics route (often S-shaped or even mesh-shaped)., which will add a lot of unnecessary investment and trouble.
(7) Matching of personnel and equipment
No matter how high the degree of automation of the automated warehouse is, specific operations still require a certain amount of manual labor, so the number of staff must be appropriate. Not enough staff will reduce the efficiency of the warehouse, and too many will cause waste. Automated warehouses use a large number of advanced equipment, so the quality requirements for personnel are relatively high. If the quality of personnel cannot keep up, it will also reduce the throughput capacity of the warehouse. Third-party logistics companies need to recruit specialized talents and provide them with specialized training.
(8) Transmission of system data
Due to reasons such as unblocked data transmission paths or data redundancy, the system data transmission speed may be slow or even impossible. Therefore, the problem of information transmission within the automated warehouse and between the upper and lower management systems of third-party logistics enterprises must be considered.
(9) Overall operational capabilities
The coordination of the upstream, downstream and internal subsystems of the automated warehouse has a problem of the barrel effect, that is, the shortest piece of wood determines the capacity of the barrel. Some warehouses use a lot of high-tech products and have very complete facilities and equipment. However, due to poor coordination and compatibility between various subsystems, the overall operational capacity is much worse than expected.
Control System
With advanced technology, the direct communication method of on-site control bus is adopted, so that the computer can only monitor but not control. All decision-making, job scheduling and on-site information are communicated by on-site equipment such as stackers and inbound and outbound conveyors through mutual communication. Coordination is complete.
● The pallet number of each cargo location is recorded in the database of the stacker and the computer respectively. The administrator can use the comparison function to compare the computer records and the records in the stacker and make modifications. The modifications can be completed automatically or manually.
● The system software and hardware have complete functions, the user interface is clear, and it is easy to operate and maintain.
● The stacker has the function of automatically recalling the origin, that is, no matter what the situation, as long as the fork is centered and horizontally running normally, it can automatically return to the origin according to the issued command. This means that operators and maintenance personnel can avoid entering the tunnel as much as possible.
●The intelligent control system can realize the true automatic inventory function, avoiding the heavy manual inventory work in the past, reducing the work intensity of warehouse managers, and ensuring that the error rate of outbound operations is zero.
Monitoring and management system
The monitoring and management system includes modules such as data management, warehousing management, outbound management, query, report, document and inventory, alarm, monitoring and animation.
Application areas
Automated warehouses are widely used in global. An overview is as follows:
Industrial production field
1 Pharmaceutical production: Pharmaceutical production is one of the earliest fields to apply automated warehouses. In 1993, Guangzhou Yangcheng Pharmaceutical Factory built China's earliest automated warehouse for pharmaceutical production. Since then, dozens of companies such as Jilin Aodong, Northeast Pharmaceutical, Yangzijiang Pharmaceutical, Shijiazhuang Pharmaceutical, and Shanghai Pharmaceuticals Group have successfully applied automated three-dimensional libraries.
2 Automobile manufacturing: one of the earliest fields in China to apply automated warehouses. China Second Automotive Industry Corporation was the first unit to apply automated warehouses. China's major automobile manufacturing companies almost without exception use automated three-dimensional libraries.
3. Machinery manufacturing : It is one of the fields where automated warehouses are widely used. Such as Sany Heavy Industry, etc.
4 Electronic manufacturing: Lenovo and other electronic fields began to adopt automated warehouse systems after 2000.
5 Tobacco manufacturing industry: The most common industry in China that adopts automated warehouses. And a large number of imported equipment are used. Typical ones include Honghe and Changsha.
Logistics field
1 Tobacco distribution: Automated warehouse systems are widely used.
2 Pharmaceutical distribution: In response to GSP certification, a large number of automated warehouses have been applied to the national pharmaceutical distribution field. Such as traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Chinese medicine, etc.
3 Airport freight: an area that adopted automated warehouses early. All major airports use three-dimensional warehouse systems for baggage handling.
4 Subway: With the boom of subway construction in China, the application of automated warehouses has been widely spread.
Commodity manufacturing field
1 Clothing: The application of automated three-dimensional libraries in the clothing field has happened in recent years.
2 Wine: such as Yanghe, Niulanshan, etc.
3 Milk: Mengniu, Yili and other companies have applications.
4 Chemical industry: one of the earliest industries to apply automated warehouses.
5 Printing, publishing, and books: it is also one of the widely used industries.
military applications
One of the most common areas where automated stereo libraries are used. Logistics, equipment, etc. are particularly common.
other
In addition, there are many fields where automated three-dimensional libraries are applied. Such as core library, tire library, teaching library, etc. Due to space limitations, we will not give examples one by one.
Shipping method
Project general contracting (design, manufacturing, installation, commissioning, service) or control and management system subcontracting.
Component
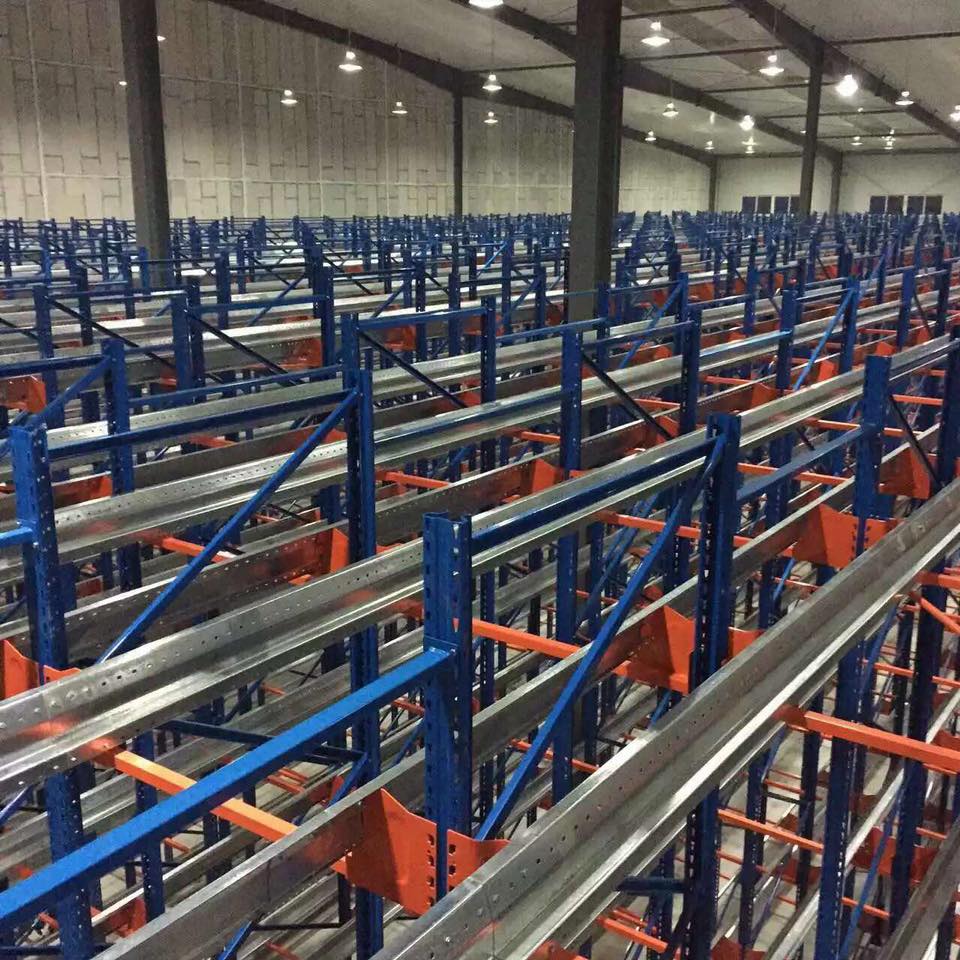
1. Shelves : Steel structures used to store goods. There are two basic forms: welded shelves and combined shelves.
2. Pallet (cargo box): a device used to carry goods, also called work station equipment.
3. Lane stacker: equipment used for automatic storage and retrieval of goods. According to the structural form, it is divided into two basic forms: single column and double column; according to the service mode, it is divided into three basic forms: straight road, curve and transfer car.
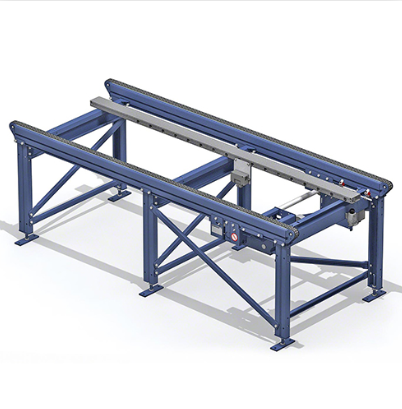
4. Conveyor system: The main peripheral equipment of the three-dimensional warehouse, responsible for transporting goods to or removing goods from the stacker. There are many types of conveyors, the common ones include roller conveyors, chain conveyors, lifting tables, distribution trucks, elevators, belt conveyors, etc.
5. AGV system: automatic guided vehicle. According to its guiding method, it is divided into induction guided trolley and laser guided trolley.
6. Automatic control system : the automatic control system that drives each equipment of the automated warehouse system. Mainly adopt fieldbus method as the control mode.
7. Storage information management system : also known as central computer management system. It is the core of the fully automated warehouse system. Typical automated three-dimensional library systems use large database systems (such as ORACLE, SYBASE, etc.) to build typical client /server systems, which can be networked or integrated with other systems (such as ERP systems, etc.).
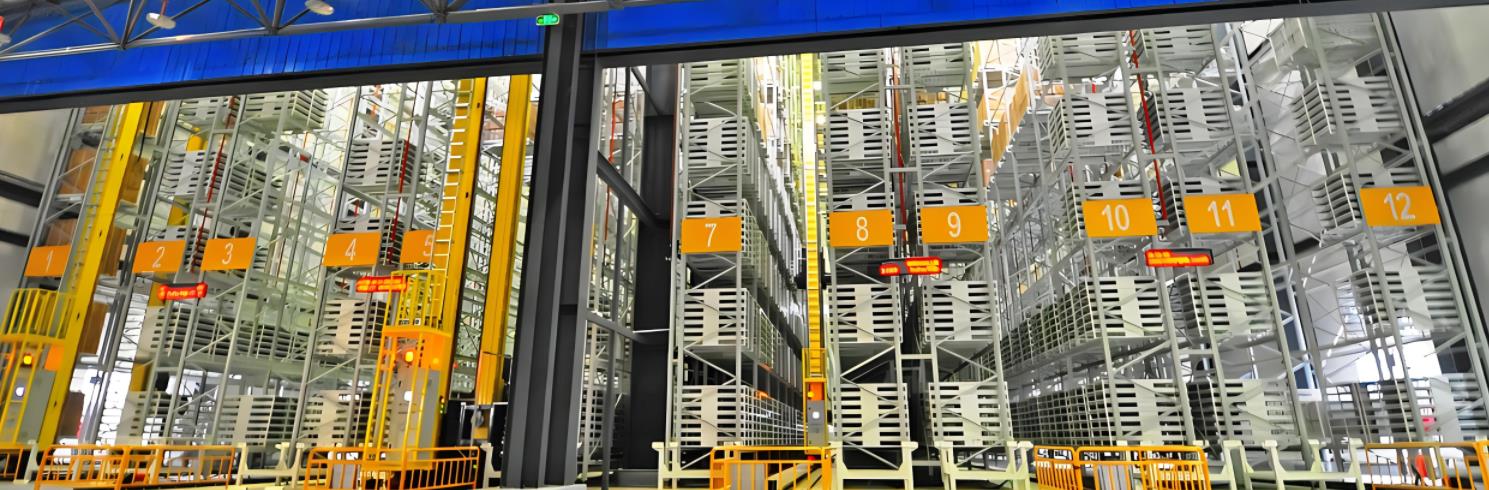

Superior performance
The advantages of automated warehouses are multifaceted. For enterprises, they can be reflected in the following aspects:
1. Improve space utilization
The basic starting point of the early three-dimensional warehouse concept was to improve space utilization and fully save limited and precious land. In some developed countries in the West, the concept of improving space utilization has broader and profound implications. Saving land has been linked to energy conservation, environmental protection and other aspects. Some even regard space utilization as an important indicator for evaluating the rationality and advancement of the system.
The space utilization of the three-dimensional warehouse is closely related to its planning. Generally speaking, the space utilization rate of automated elevated warehouses is 2-5 times that of ordinary flat warehouses. This is quite impressive.
2. Facilitate the formation of advanced logistics systems and improve the level of enterprise production management
Traditional warehouses are just places where goods are stored. Preserving goods is its only function, and it is a kind of "static storage". The automated warehouse uses advanced automated material handling equipment, which not only allows goods to be automatically accessed and retrieved as needed in the warehouse, but also can be organically connected to the production links outside the warehouse, and through computer management systems and automated material handling equipment, the warehouse becomes An important link in enterprise production logistics. The storage of outsourced parts and self-produced parts by enterprises in automated warehouses is a link in the entire production. Short-term storage is to automatically output to the next process for production at a designated time, thus forming an automated logistics system. This is a " "Dynamic storage" is also an obvious technological trend in the development of today's automated warehouses.
The above-mentioned logistics system is a subsystem of the entire enterprise production management system (from ordering, necessary design and planning, planning and production arrangements, manufacturing, assembly, testing, shipping, etc.). The logistics system is established in conjunction with the enterprise. Real-time connection between systems is another obvious technological trend in the development of automated high-bay warehouses.
Reasons why automated warehouses are rare in China:
Since China's first self-developed automated warehouse was put into production in 1980, its application in the automotive, chemical, electronics, tobacco and other industries has increased year by year.
Development status
In today's world of high human resource costs, reducing the costs of an enterprise and realizing automated management have become an important strategic topic for enterprise research. For the manufacturing industry, logistics costs account for a considerable proportion of its costs. Statistics show that logistics costs usually account for more than 50% of manufacturing costs. Therefore, material and warehousing management and cost control have become factors affecting product market competitiveness. The key is inseparable from the efficiency of the enterprise.
Since the operating efficiency and automation technical level of automated warehouses can greatly improve the logistics efficiency of enterprises, and the basic technology of three-dimensional warehouses has become increasingly mature, more and more companies have begun to adopt automated warehouses. Many companies not only build medium and large three-dimensional warehouses, but also build many small and medium-sized automated warehouses according to needs.
The emergence and development of automated warehouses were the result of production and technological development after World War II. In the early 1950s, three-dimensional warehouses using bridge stacker cranes emerged in the United States; In the late 1950s and early 1960s, an automated warehouse with a driver operated aisle style stacker crane emerged; In 1963, the United States was the first to adopt computer control technology in elevated warehouses and established the first computer-controlled automated warehouse. Subsequently, automated warehouses developed rapidly in the United States and Europe, forming specialized disciplines. In the mid-1960s, Japan began building automated warehouses and its development speed became increasingly fast, becoming one of the countries with the most automated warehouses in the world today. The development of automated warehouses and their material handling equipment in China began not too late. In 1963, the first bridge stacker crane was developed (Beijing Institute of Lifting and Transportation Machinery of the Ministry of Machinery). In 1973, China began to develop the first computer-controlled automated warehouse (15 meters high, responsible for lifting by the Ministry of Machinery). The system was put into operation in 1980. As of 2009, the number of automated warehouses in China has exceeded 1200. Due to its high space utilization, strong inbound and outbound capabilities, and the use of computers for control and management, automated warehouses have become an indispensable warehousing technology for enterprise logistics and production management, and are increasingly valued by enterprises.
2012 was a year in which China's automated warehouses developed rapidly. At the beginning of 2012, due to the commencement of many logistics system engineering projects, the construction market of automated warehouse projects was booming. According to incomplete statistics, there were more than 130 large-scale three-dimensional warehouse projects under construction in 2012. As of December 2012, In September, the number of automated warehouses nationwide exceeded 1,200.
With the continued improvement of the national economy and the continued rapid growth of tobacco, medicine, machinery and other industries that have high demand for automated warehouses, automated warehouses will face greater market demand in the future. Take the pharmaceutical industry as an example. According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics, as of 2012, the number of enterprises with a total industrial output value of more than 20 million in China was 6,075. Calculated at 10% of the demand, the demand for automated warehouses in the pharmaceutical industry is There are 607 units, and the number of units in stock is less than 200. The market prospects are promising.
Warehouse design
With the acceleration of economic globalization, the huge potential contained in the logistics supply chain has attracted more and more people's attention. The logistics center is one of the important hubs in the logistics supply chain. It is a facility and institution that accepts and processes ordering information from downstream users, conducts centralized storage and processing of large quantities of goods from upstream suppliers, and conducts bulk transfers to downstream. The direct execution agencies that implement these functions include:
(1) Automatic storage equipment (automated warehouse)
(2) Other shelves (flat pallet shelves, mobile shelves, etc.)
(3) Various conveyors ( roller conveyors, chain conveyors, belt conveyors, lifting transfer machines, elevators, etc.)
(4) Various sorting equipment
(5) Unmanned vehicles ( AGV, RGV, LGV)
(6) Various other auxiliary equipment
As an important part of the logistics center, the Automatic Storage & Retrieval System directly affects the strategies and plans formulated by business leaders, and directs and adjusts the company's actions. Here, let’s briefly talk about its design steps, which are generally divided into the following steps:
1. Collect and study users’ original data and clarify the goals that users want to achieve. These original data include:
1. Clarify the process of connecting the automated warehouse with upstream and downstream.
2. Logistics requirements: the maximum inbound volume from the upstream into the warehouse, the maximum outbound volume for downstream transfer, and the required warehouse capacity ;
3. Material specifications: number of material varieties, material packaging form, outer packaging size, weight, storage method and other characteristics of other materials;
4. On-site conditions and environmental requirements of the three-dimensional warehouse;
5. Users' functional requirements for the warehouse management system ;
6. Other relevant information and special requirements.
2. Determine the main forms and related parameters of automated warehouses
After all the original data are collected, the relevant parameters required for design can be calculated based on these first-hand data, including: ① The total amount of incoming and outgoing of the entire warehouse area, that is, the flow requirements of the warehouse: ② The appearance of the cargo unit Dimensions and weight; ⑤ Number of positions in the warehouse storage area (shelf area): ④ Combine the above three points to determine the number of rows, columns and lanes of shelves in the storage area (shelf factory) and other relevant technical parameters.
3. Reasonably arrange the overall layout and logistics diagram of the automated warehouse
Generally speaking, automated warehouses include: incoming temporary storage area, inspection area, palletizing area, storage area, outbound temporary storage area, pallet temporary storage area, temporary storage area for unqualified products and debris area, etc. When planning, it is not necessary to include every area mentioned above in the three-dimensional warehouse. Each area and the increase or decrease area can be reasonably divided according to the user's process characteristics and requirements. At the same time, the material flow must be reasonably considered to ensure smooth flow of materials, which will directly affect the capabilities and efficiency of the automated warehouse.
4. Select the type of mechanical equipment and related parameters
shelves
The design of the shelves is an important part of the three-dimensional warehouse design, which directly affects the area and space utilization of the three-dimensional warehouse.
①Shelf form: There are many forms of shelves, and the shelves used in automated warehouses generally include: beam shelves, corbel-type shelves, mobile shelves, etc. When designing, reasonable selection can be made based on the overall dimensions, weight and other related factors of the cargo unit.
②The size of the cargo compartment: The size of the cargo compartment depends on the size of the gap between the cargo unit and the shelf columns and beams ( corbels ). To a certain extent, it is also affected by the shelf structure type and other factors.
stacker crane
The stacker is the core equipment of the entire automated warehouse. It can transport goods from one place to another through manual operation, semi-automatic operation or fully automatic operation. It consists of a frame (upper beam, lower beam, column), horizontal traveling mechanism, lifting mechanism, cargo platform, cargo forks and electrical control system.
① Determination of the form of stacker: There are various forms of stacker, including single- track tunnel stacker, double-track tunnel stacker, rotating tunnel stacker, single-column stacker, double-column stacker, etc. wait.
② Determination of stacker speed: According to the flow requirements of the warehouse, calculate the horizontal speed, lifting speed and fork speed of the stacker.
③Other parameters and configuration: Select the positioning method and communication method of the stacker according to the warehouse site conditions and user requirements. The configuration of the stacker crane can be high or low, depending on the situation.
Conveyor system
According to the logistics diagram, reasonably select the type of conveyor, including: roller conveyor, chain conveyor, belt conveyor, lift transfer machine, elevator, etc. At the same time, the speed of the conveyor system must be reasonably determined based on the instantaneous flow of the warehouse.
Other equipment
According to the process flow of the warehouse and some special requirements of users, some auxiliary equipment can be added appropriately, including: handheld terminals, forklifts, balancing cranes, etc.
5. Preliminary design of each functional module of the control system and warehouse management system ( WMS )
According to the warehouse's process flow and user requirements, the control system and warehouse management system (WMS) are reasonably designed. Control systems and warehouse management systems generally adopt modular designs to facilitate upgrades and maintenance.
6. Simulation of the entire system
If possible, simulating the entire system can provide a more intuitive description of the storage and transportation work of the three-dimensional warehouse, discover some of the problems and deficiencies, and make corresponding corrections to optimize the entire AS/RS system.
7. Carry out detailed design of equipment and control management systems
The above is the general process of designing an automated warehouse. In the specific design, it can be used flexibly according to the specific situation.
System advantages
1. Save the warehouse floor space and make full use of the warehouse space. Since the automated warehouse uses the assembly of large-scale storage shelves, coupled with automated management technology, the goods are easy to find. Therefore, the construction of an automated warehouse requires a smaller area than a traditional warehouse, but the space utilization rate is high. In developed countries, improving space utilization has become an important assessment indicator for the rationality and advancement of the system. Today, when energy conservation and environmental protection are advocated, automated warehouses have a very good effect in saving floor space resources, and it is also a major trend that will surely lead to future warehousing development.
2. Automated management improves the management level of the warehouse. The automated warehouse uses computers to conduct accurate information management of goods information, reducing errors that may occur in storing goods and improving work efficiency. At the same time, the three-dimensional automated warehouse realizes motorization in the transportation of goods into and out of the warehouse, making the transportation work safe and reliable, reducing the damage rate of goods, and through special design, some goods with special environmental requirements can be well preserved. The environment, such as toxic and explosive goods, also reduces the injuries that people may suffer when handling goods.
3. Automated warehouses can form an advanced production chain and promote the advancement of productivity. Professionals pointed out that due to the high access efficiency of automated warehouses, they can effectively connect the warehouse's off-site production links and form an automated logistics system in storage, thereby forming a planned and arranged production chain, which greatly improves production capacity. increase in magnitude.
Companies that specialize in building automated warehouses
There are several companies that specialize in building automated warehouses and providing solutions for warehouse automation. Here are some notable companies in this field:
1. Dematic: Dematic is a global leader in providing intelligent automation solutions for supply chain optimization. They offer a range of automated warehouse solutions, including automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), conveyor systems, sorting systems, and robotics.
2. Swisslog: Swisslog is a provider of automated intralogistics solutions, including warehouse automation systems. Their offerings include automated storage and retrieval systems, robotic picking systems, shuttle systems, and software solutions for warehouse management and control.
3. Honeywell Intelligrated: Honeywell Intelligrated specializes in warehouse automation and material handling solutions. Their offerings include automated conveyor systems, robotic solutions, AS/RS systems, and software for warehouse optimization.
4. SSI Schaefer: SSI Schaefer is a global provider of warehouse and logistics solutions. They offer a comprehensive range of products for automated warehousing, including AS/RS systems, conveying systems, picking systems, and software solutions.
5. Vanderlande: Vanderlande is a leading provider of automated material handling systems and solutions for warehouses and distribution centers. Their offerings include conveyor systems, robotic solutions, sorting systems, and baggage handling systems.
6. KION Group: KION Group is a provider of intralogistics solutions, including warehouse automation solutions. They offer a range of automated material handling equipment, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs), pallet trucks, and stackers.
7. Daifuku: Daifuku is a global company specializing in material handling systems and warehouse automation. They provide a wide range of solutions, including AS/RS systems, conveyor systems, sorting systems, and robotic solutions.
8. Bastian Solutions: Bastian Solutions is a material handling systems integrator that offers customized warehouse automation solutions. They provide a variety of automation technologies, including conveyor systems, robotics, AS/RS systems, and order fulfillment solutions.
9. Ebil Tech: "EBILTECH" for short, is committed to the planning, design, system integration, project implementation and after-sales service for automation three-dimensional warehousing logistics projects. With its headquarter located in Gaochun High-tech Development Zone,Jiangsu.
These companies are known for their expertise in designing, implementing, and supporting automated warehouse solutions. However, it's important to note that the warehouse automation industry is dynamic, and new companies may emerge while existing companies continue to evolve their offerings.